js
overview
js(browser-runtime):
现代javascript;
mdn;nodejs:
参考笔记1:https://github.com/tangzixuan/nodebestpractices;
参考笔记2:link1 -- link2;
参考笔记3:link1 -- link2;
core-content
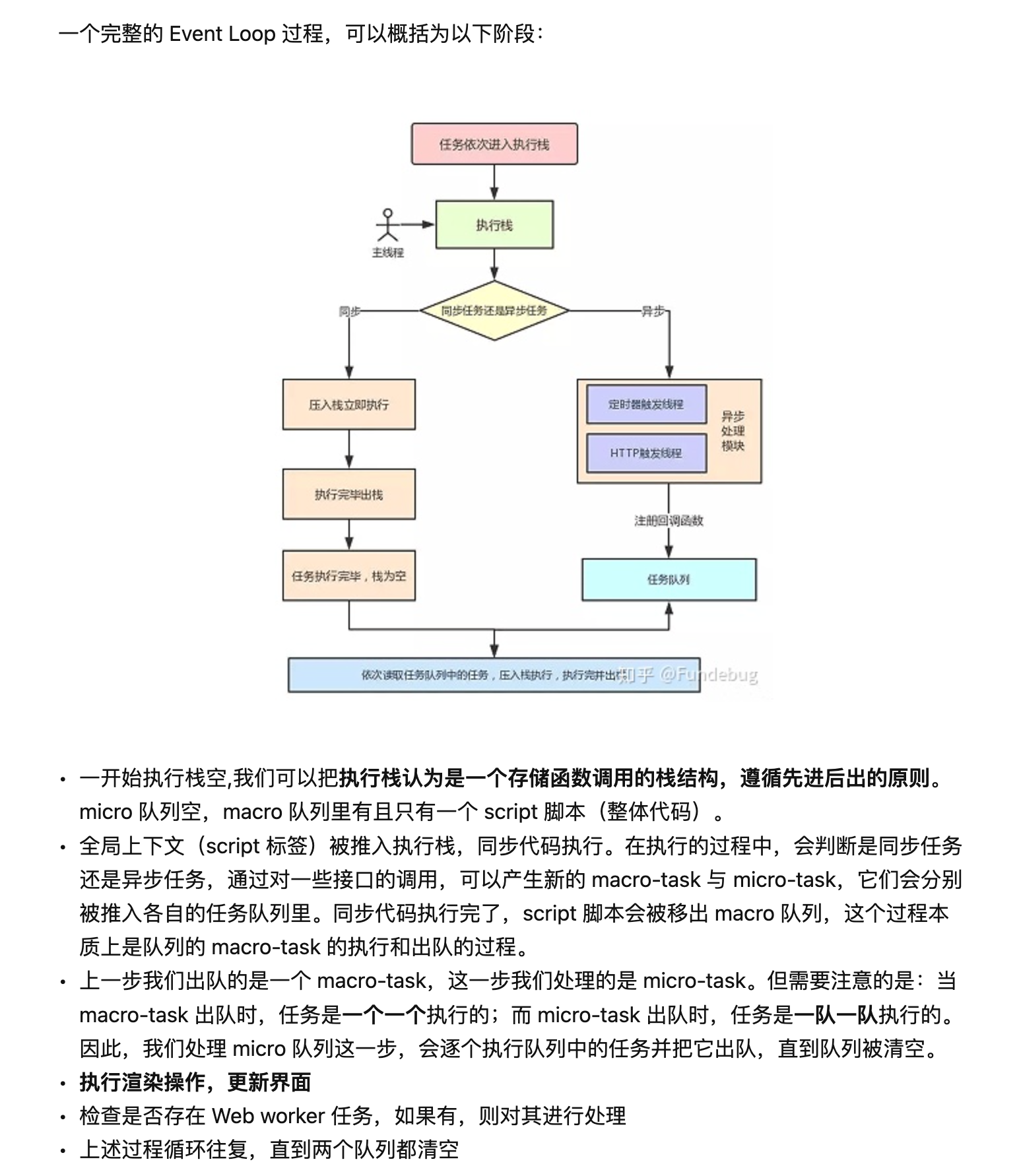
event-loop
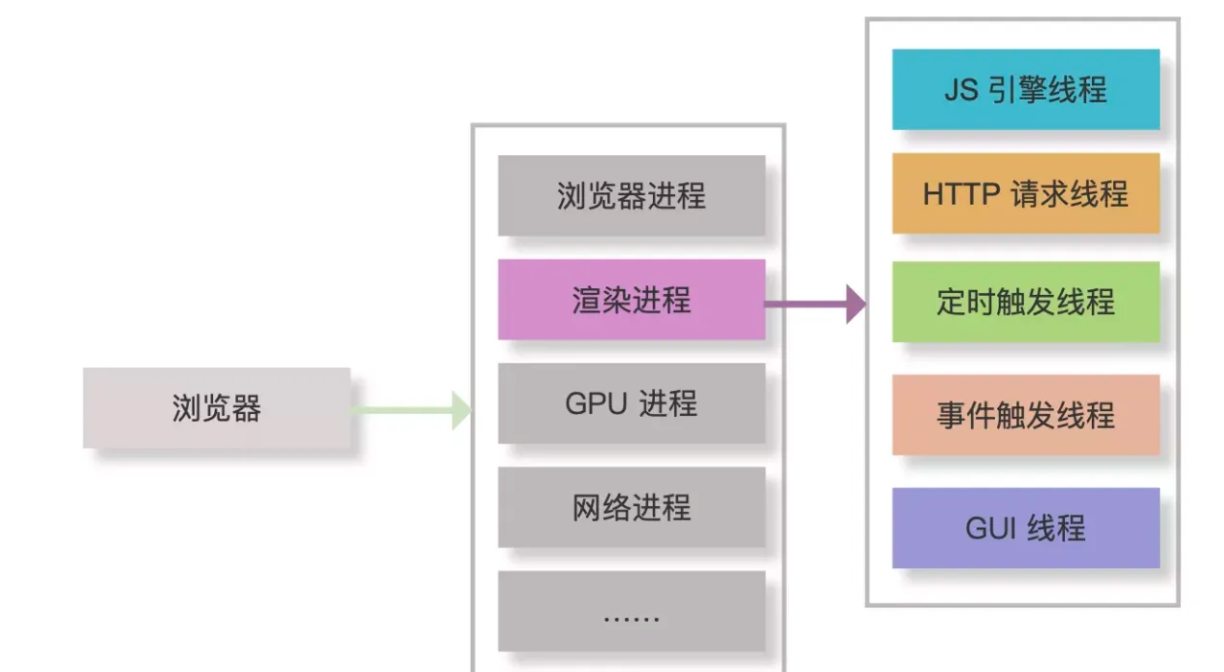
browser-runtime
- 参考资源: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/580956436
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/48522249
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/54882306 - 参考机制图解:

- 备注: setImmediate 和 Process.nextTick() 在浏览器中是不存在的,因为浏览器中没有事件循环的概念,所以也就没有了这两个方法,在nodejs环境下才支持。
requestAnimationFrame
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/window/requestAnimationFrame
- https://www.zhihu.com/question/456804188
- https://juejin.cn/post/7202935318457942071
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/267273074
requestIdleCallback
- https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/API/Window/requestIdleCallback
- https://www.zhihu.com/question/434791954/answer/2453356416
EventLoop 和浏览器渲染、帧动画、空闲回调的关系
- 这个写的非常好:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/142742003,而且非常重要


node-runtime
- 参考:
https://nodejs.org/en/learn/asynchronous-work/event-loop-timers-and-nexttick
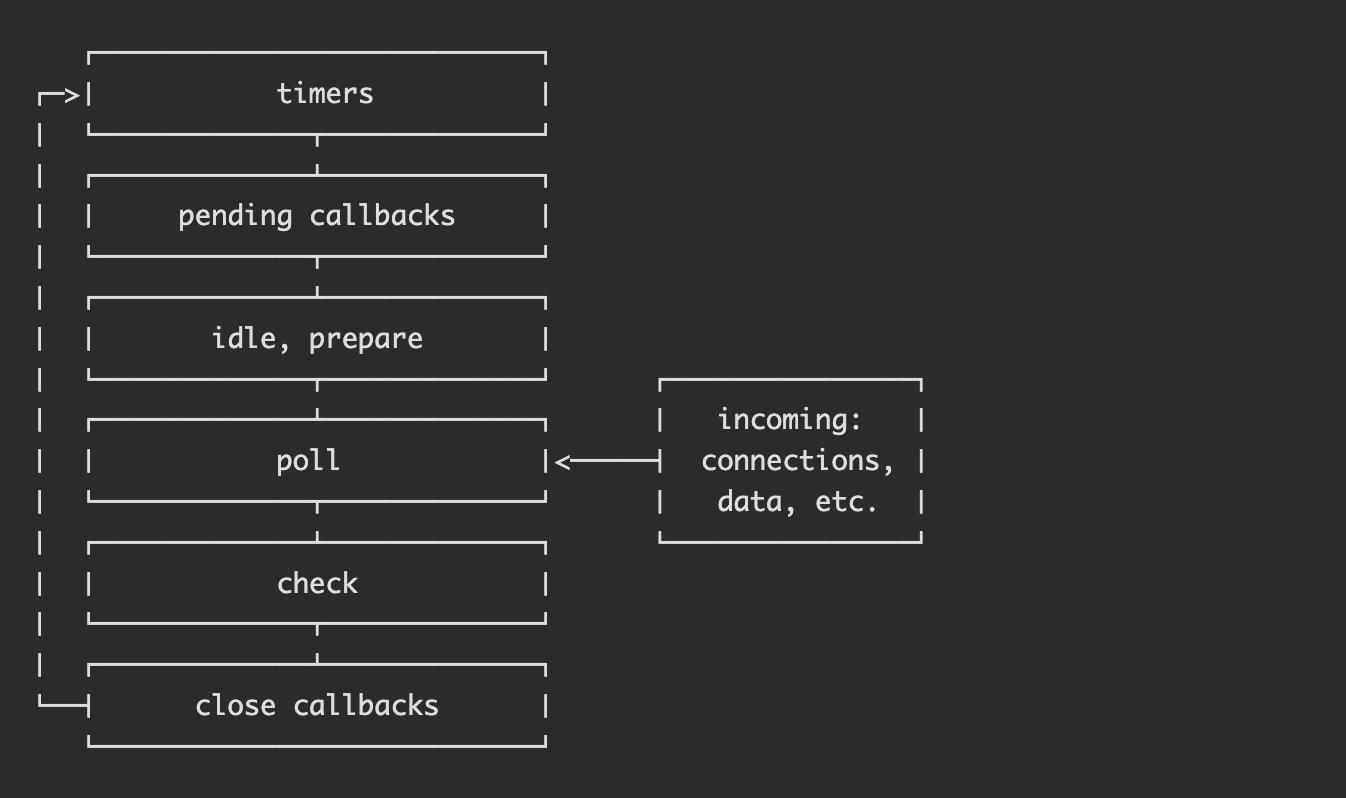
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/35918797 - Phases Overview:
timers: this phase executes callbacks scheduled by setTimeout() and setInterval().
pending callbacks: executes I/O callbacks deferred to the next loop iteration.
idle, prepare: only used internally.
poll: retrieve new I/O events; execute I/O related callbacks (almost all with the exception of close callbacks, the ones scheduled by timers, and setImmediate()); node will block here when appropriate.
check: setImmediate() callbacks are invoked here.
close callbacks: some close callbacks, e.g. socket.on('close', ...). - 参考机制图解:
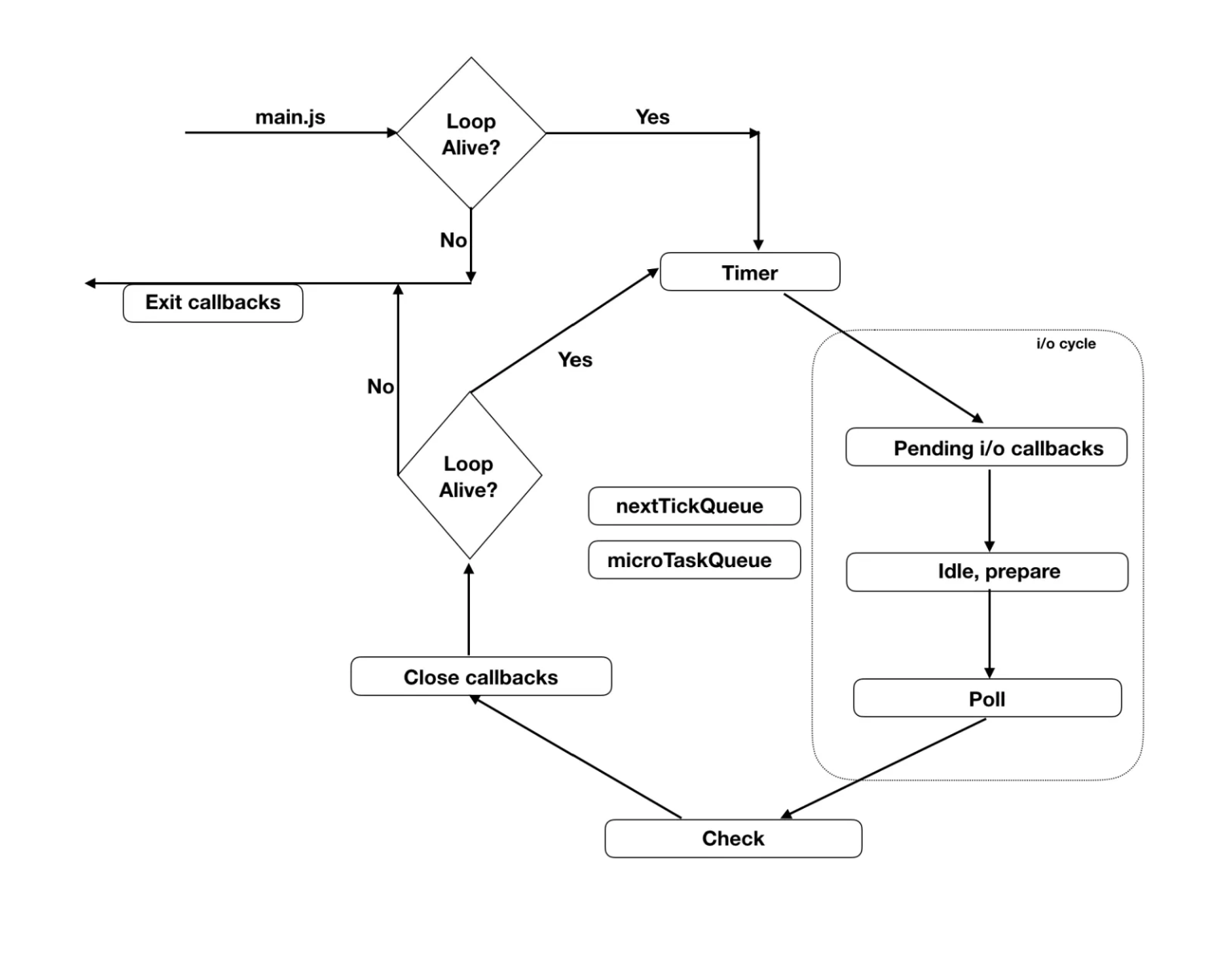
输入输出判断
- q1:
js
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('setTimeout start');
new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log('promise1 start');
resolve();
}).then(() => {
console.log('promise1 end');
})
console.log('setTimeout end');
}, 0);
function promise2() {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
console.log('promise2');
resolve();
})
}
async function async1() {
console.log('async1 start');
await promise2();
console.log('async1 end');
}
async1();
console.log('script end');- q2:
js
const fs = require('fs');
fs.readFile(__filename, (data) => {
// poll(I/O 回调) 阶段
console.log('readFile')
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.error('promise1')
})
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.error('promise2')
})
});
setTimeout(() => {
// timers 阶段
console.log('timeout');
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.error('promise3')
})
Promise.resolve().then(() => {
console.error('promise4')
})
}, 0);
// 下面代码只是为了同步阻塞1秒钟,确保上面的异步任务已经准备好了
var startTime = new Date().getTime();
var endTime = startTime;
while(endTime - startTime < 1000) {
endTime = new Date().getTime();
}
// 最终输出 timeout promise3 promise4 readFile promise1 promise2- await一个同步函数
js
console.log('start');
setTimeout(() => {
console.log('timeout');
}, 0);
new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
console.log('promise测试');
resolve()
console.log('promise测试 after for-loop');
}).then(() => {
console.log('promise测试1');
}).then(() => {
console.log('promise测试2');
})
function fn1() {
console.log('await 1')
}
async function fn() {
console.log('fn start')
const res = await fn1()
console.log('fn end')
}
fn()
console.log('end');- 微任务事件: 执行时产生了微任务,会继续丢到微任务队列中去;
js
const genMicroTask = (value)=> {
new Promise((resolve)=>{
resolve(1)
}).then(()=>{
console.log("test1",value)
})
}
new Promise((resolve)=> {
resolve(1)
}).then((value)=>{
console.log(2)
genMicroTask(3)
setTimeout(()=> {
console.log(4)
},0)
genMicroTask(5)
})浏览器性能分析
- performance:
https://juejin.cn/post/6850S418121548365831; - react devtools profile面板;
- chrome lighthouse:
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/376925215;
js-bridge
- https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/438763800;
- Native->Web:
首先来说Native端调用Web端,这个比较简单,JavaScript作为解释性语言,最大的一个特性就是可以随时随地地通过解释器执行一段JS代码,所以可以将拼接的JavaScript代码字符串,传入JS解析器执行就可以,JS解析器在这里就是webView;
- Web->Native:
拦截Webview请求的URL Schema;向Webview中注入JS API;
同源和跨域
微前端
- 微前端js沙箱:https://juejin.cn/post/6981374562877308936;
- 微前端乾坤:https://juejin.cn/post/7070032850237521956;
低代码
- 阿里低代码引擎:
https://lowcode-engine.cn/site/docs/guide/quickStart/intro;
https://github.com/alibaba/lowcode-engine;
js基础
闭包
- 概念:
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Closures;
https://zh.javascript.info/closure; - 闭包陷阱:
https://juejin.cn/post/7093699777556119565; - 闭包的示例:
js
const fn = () => {
let increment = 0;
const add = () => {
increment++;
console.log(increment);
}
console.log('fn() called', increment);
return [increment, add]
}
const [increment, add] = fn();
console.log(increment);
add();
add();
add();
console.log(increment);
const fn1 = () => {
let obj = {
increment: 0
};
const add1 = () => {
obj.increment++;
console.log(obj);
}
console.log('fn() called', obj);
return [obj, add1]
}
const [obj, add1] = fn1();
console.log(obj);
add1();
console.log(increment);promise
手写一个promise简化版本: https://juejin.cn/post/6850037281206566919#heading-2;
version1:
sh
const PENDING = 'PENDING';
const FULFILLED = 'FULFILLED';
const REJECTED = 'REJECTED';
class Promise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
// 存放成功的回调
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
// 存放失败的回调
this.onRejectedCallbacks= [];
let resolve = (value) => {
if(this.status === PENDING) {
this.status = FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
// 依次将对应的函数执行
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach(fn=>fn());
}
}
let reject = (reason) => {
if(this.status === PENDING) {
this.status = REJECTED;
this.reason = reason;
// 依次将对应的函数执行
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach(fn=>fn());
}
}
try {
executor(resolve,reject)
} catch (error) {
reject(error)
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
if (this.status === FULFILLED) {
onFulfilled(this.value)
}
if (this.status === REJECTED) {
onRejected(this.reason)
}
if (this.status === PENDING) {
// 如果promise的状态是 pending,需要将 onFulfilled 和 onRejected 函数存放起来,等待状态确定后,再依次将对应的函数执行
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
onFulfilled(this.value)
});
// 如果promise的状态是 pending,需要将 onFulfilled 和 onRejected 函数存放起来,等待状态确定后,再依次将对应的函数执行
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(()=> {
onRejected(this.reason);
})
}
}
}- version2:
sh
const PENDING = "PENDING";
const FULFILLED = "FULFILLED";
const REJECTED = "REJECTED";
const resolvePromise = (promise2, x, resolve, reject) => {
// 自己等待自己完成是错误的实现,用一个类型错误,结束掉 promise Promise/A+ 2.3.1
if (promise2 === x) {
return reject(
new TypeError("Chaining cycle detected for promise #<Promise>")
);
}
// Promise/A+ 2.3.3.3.3 只能调用一次
let called;
// 后续的条件要严格判断 保证代码能和别的库一起使用
if ((typeof x === "object" && x != null) || typeof x === "function") {
try {
// 为了判断 resolve 过的就不用再 reject 了(比如 reject 和 resolve 同时调用的时候) Promise/A+ 2.3.3.1
let then = x.then;
if (typeof then === "function") {
// 不要写成 x.then,直接 then.call 就可以了 因为 x.then 会再次取值,Object.defineProperty Promise/A+ 2.3.3.3
then.call(
x,
(y) => {
// 根据 promise 的状态决定是成功还是失败
if (called) return;
called = true;
// 递归解析的过程(因为可能 promise 中还有 promise) Promise/A+ 2.3.3.3.1
resolvePromise(promise2, y, resolve, reject);
},
(r) => {
// 只要失败就失败 Promise/A+ 2.3.3.3.2
if (called) return;
called = true;
reject(r);
}
);
} else {
// 如果 x.then 是个普通值就直接返回 resolve 作为结果 Promise/A+ 2.3.3.4
resolve(x);
}
} catch (e) {
// Promise/A+ 2.3.3.2
if (called) return;
called = true;
reject(e);
}
} else {
// 如果 x 是个普通值就直接返回 resolve 作为结果 Promise/A+ 2.3.4
resolve(x);
}
};
class Promise {
constructor(executor) {
this.status = PENDING;
this.value = undefined;
this.reason = undefined;
this.onResolvedCallbacks = [];
this.onRejectedCallbacks = [];
let resolve = (value) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.status = FULFILLED;
this.value = value;
this.onResolvedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => fn());
}
};
let reject = (reason) => {
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.status = REJECTED;
this.reason = reason;
this.onRejectedCallbacks.forEach((fn) => fn());
}
};
try {
executor(resolve, reject);
} catch (error) {
reject(error);
}
}
then(onFulfilled, onRejected) {
//解决 onFufilled,onRejected 没有传值的问题
//Promise/A+ 2.2.1 / Promise/A+ 2.2.5 / Promise/A+ 2.2.7.3 / Promise/A+ 2.2.7.4
onFulfilled = typeof onFulfilled === "function" ? onFulfilled : (v) => v;
//因为错误的值要让后面访问到,所以这里也要跑出个错误,不然会在之后 then 的 resolve 中捕获
onRejected =
typeof onRejected === "function"
? onRejected
: (err) => {
throw err;
};
// 每次调用 then 都返回一个新的 promise Promise/A+ 2.2.7
let promise2 = new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
if (this.status === FULFILLED) {
//Promise/A+ 2.2.2
//Promise/A+ 2.2.4 --- setTimeout
setTimeout(() => {
try {
//Promise/A+ 2.2.7.1
let x = onFulfilled(this.value);
// x可能是一个proimise
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (e) {
//Promise/A+ 2.2.7.2
reject(e);
}
}, 0);
}
if (this.status === REJECTED) {
//Promise/A+ 2.2.3
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = onRejected(this.reason);
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
}, 0);
}
if (this.status === PENDING) {
this.onResolvedCallbacks.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = onFulfilled(this.value);
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
}, 0);
});
this.onRejectedCallbacks.push(() => {
setTimeout(() => {
try {
let x = onRejected(this.reason);
resolvePromise(promise2, x, resolve, reject);
} catch (e) {
reject(e);
}
}, 0);
});
}
});
return promise2;
}
}
Promise.prototype.catch = function (errCallback) {
return this.then(null, errCallback);
};
Promise.prototype.finally = function (callback) {
return this.then(
(value) => {
return Promise.resolve(callback()).then(() => value);
},
(reason) => {
return Promise.resolve(callback()).then(() => {
throw reason;
});
}
);
};
Promise.all = function (values) {
if (!Array.isArray(values)) {
const type = typeof values;
return new TypeError(`TypeError: ${type} ${values} is not iterable`);
}
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
let resultArr = [];
let orderIndex = 0;
const processResultByKey = (value, index) => {
resultArr[index] = value;
if (++orderIndex === values.length) {
resolve(resultArr);
}
};
for (let i = 0; i < values.length; i++) {
let value = values[i];
if (value && typeof value.then === "function") {
value.then((value) => {
processResultByKey(value, i);
}, reject);
} else {
processResultByKey(value, i);
}
}
});
};
Promise.race = function (promises) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 一起执行就是for循环
for (let i = 0; i < promises.length; i++) {
let val = promises[i];
if (val && typeof val.then === "function") {
val.then(resolve, reject);
} else {
// 普通值
resolve(val);
}
}
});
};
const promisify = (fn) => {
// 典型的高阶函数 参数是函数 返回值是函数
return (...args) => {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
fn(...args, function (err, data) {
// node中的回调函数的参数 第一个永远是error
if (err) return reject(err);
resolve(data);
});
});
};
};promise链式调用
- 题目:
js
fetched(0, () => {
console.log(1);
});
fetched(500, () => {
console.log(2);
});
fetched(100, () => {
console.log(3);
});
fetched(200, () => {
console.log(4);
});
// output: 1, 2, 3, 4js
let originPromise = Promise.resolve();
const fetched = (time, cb) => {
originPromise = originPromise.then(() => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
setTimeout(() => {
cb();
resolve();
}, time);
});
});
}
fetched(0, () => {
console.log(1);
});
fetched(500, () => {
console.log(2);
});
fetched(100, () => {
console.log(3);
});
fetched(200, () => {
console.log(4);
});js并发限制多个请求
js
// 并发请求函数
const concurrencyRequest = (urls, maxNum) => {
return new Promise((resolve) => {
if (urls.length === 0) {
resolve([]);
return;
}
const results = [];
let index = 0; // 下一个请求的下标
let count = 0; // 当前请求完成的数量
// 发送请求
async function request() {
if (index === urls.length) return;
const i = index; // 保存序号,使result和urls相对应
const url = urls[index];
index++;
console.log(url);
try {
const resp = await fetch(url);
// resp 加入到results
results[i] = resp;
} catch (err) {
// err 加入到results
results[i] = err;
} finally {
count++;
// 判断是否所有的请求都已完成
if (count === urls.length) {
console.log('完成了');
resolve(results);
}
request();
}
}
// maxNum和urls.length取最小进行调用
const times = Math.min(maxNum, urls.length);
for(let i = 0; i < times; i++) {
request();
}
})
}js最大同时请求限制
js
const realFetch = (...arg)=> {
return fetch(arg)
}
const queue = []
const maxCurrentFetchLimit = 5
let currentFetchNum = 0
const checkCurrentFetchNum = () => currentFetchNum < maxCurrentFetchLimit;
const editCurrentFetchNum = (arg) => {
currentFetchNum = currentFetchNum + arg
}
const fetch = (...args) => {
return new Promise((resolve,reject)=> {
const newRequest = {
arg: args,
// id: String(Date.now()) + Math.random(100),
resolveCb: resolve,
rejectCb: reject
}
queue.push(newRequest);
})
}
setInterval(()=> {
if(queue.length > 0 && checkCurrentFetchNum()) {
const req1 = queue.shift();
editCurrentFetchNum(1)
realFetch(req1.arg).then(res => {
editCurrentFetchNum(-1)
req1.resolveCb(res)
})
}
}, 0)js,blob, stream
- blob:
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/Blob;
https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/500199997; - stream:
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/API/Streams_API;
https://juejin.cn/post/6960629859827580965#heading-37;
js变量提升
js
if (!("a" in window)) {
var a = 1;
}
console.log(a); // undefined